
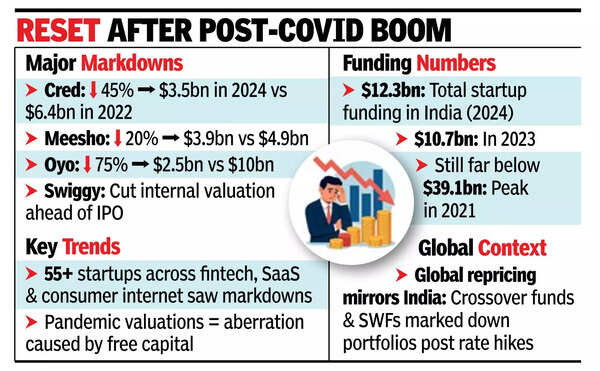
BENGALURU: Over the past two years, an increasing number of Indian startups raised capital at significantly lower valuations, reflecting a sustained reset in the late-stage venture funding market. According to data from Tracxn, at least 55 companies across sectors like fintech, SaaS, and consumer internet experienced valuation declines since January 2023.Notable markdowns include Cred, which raised $75 million in May at a valuation of approximately $3.5 billion-down nearly 45% from its 2022 peak of $6.4 billion. Meesho secured $275 million last year at a $3.9 billion valuation, reduced from $4.9 billion previously. Oyo raised $175 million in 2023 at an implied valuation of about $2.5 billion, a steep drop from its earlier high near $10 billion. Swiggy also lowered its valuation targets while preparing for its IPO, raising $46 million in 2023.
Beyond these well-known names, valuation markdowns affected a wide range of companies, including Flipkart, Pratilipi, Shiprocket, MobiKwik, GreyHR, Zolo, Lendingkart, Udaan, PayMate, Pepperfry, OfBusiness, Fisdom, and others. These adjustments spanned both primary and secondary transactions, with several companies recalibrating their private valuations in preparation for upcoming public listings.Venture investors point to a combination of inflated valuations during the 2021-2022 boom cycle and a subsequent recalibration of revenue multiples. “The fundamental problem is not with the companies themselves. Many of these companies continue to grow. The markdowns are largely a reset from highly inflated multiples that investors were willing to pay during 2021 and 2022,” said Mohan Kumar, founder and managing partner at Avataar Venture Partners.He said that SaaS companies, which saw revenue multiples of 30-100 times during the peak funding period, largely reverted to historical norms. “For late-stage SaaS companies today, if you are growing at 30% and profitable, you may command around 10 times revenue. For others, the multiple is more in the 7-8 times range. The pandemic era was an aberration where free capital distorted pricing,” Kumar added.In enterprise software, which saw some of the steepest pandemic-driven valuation spikes, multiple compression drove significant markdowns. Postman, for instance, saw secondary transactions at valuation levels 30-40% below its earlier $5.6 billion peak.Investors now broadly expect valuations to remain tied closely to profitability and revenue growth metrics.














