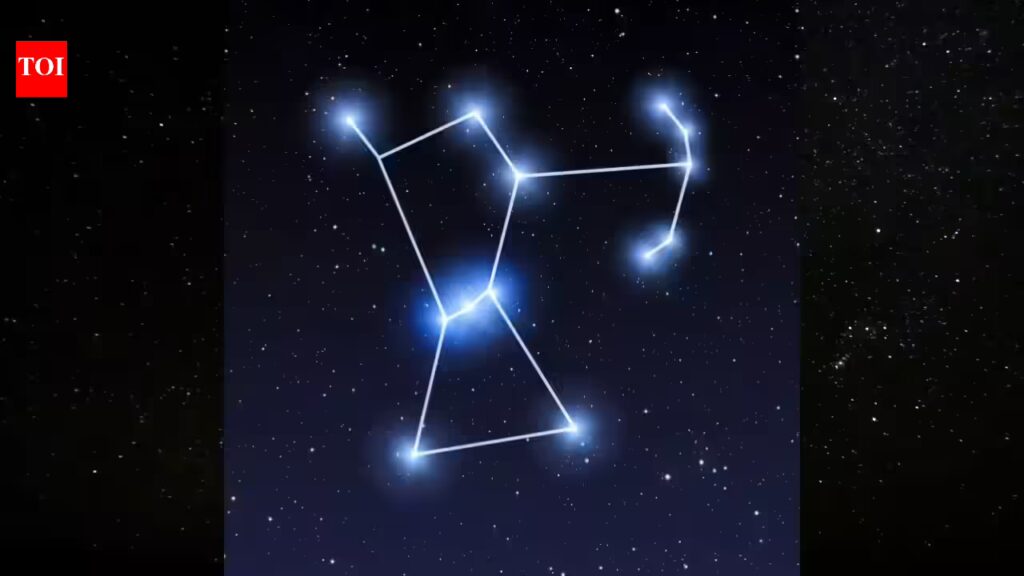
Orion’s Belt is a familiar sight in the night sky during the colder months, often noticed easily. Three bright stars sit in a straight line, rising in the east and crossing high overhead as the evening deepens. They belong to the larger Orion constellation, positioned close to the celestial equator, which makes them visible from much of the world. From Earth, the spacing appears neat and deliberate, though the stars themselves lie vast distances apart. Their brightness and alignment have made the pattern easy to recognise across centuries of observation. Astronomers classify the belt as an asterism rather than a constellation in its own right. Even so, it remains one of the most reliable reference points for locating other prominent stars.
Orion’s Belt and its role in the Hunter shape
Orion’s Belt is just three bright stars in a straight line. They are evenly spaced and easy to notice. If you look up at the night sky between October and March, chances are you have already seen them.Those three stars belong to a bigger star pattern called Orion, which people long ago imagined as a hunter. It is so easy to spot because:
- The stars are bright
- They sit in a neat straight line
- They are close together (at least from human point of view)
Your brain loves patterns, so this one jumps out almost immediately.
When and where to see Orion constellation
- Best seen in winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere
- Look towards the south after sunset
- The three stars rise in the east and set in the west
If you see three stars that look like they were drawn with a ruler, that’s probably it.
The rest of the Orion constellation
Once you find the belt, the rest of Orion becomes easy:
- Two bright stars form the “shoulders” and “feet”
- Below the belt is a faint cloudy patch called the
Orion Nebula , which you can sometimes see even without a telescope
Think of Orion like an hourglass shape, with the belt squeezed in the middle.
Using the belt as a sky map
This is the fun part:
- Follow the belt downwards and you will hit Sirius, the brightest star in the entire night sky
- Follow the belt the other way and you will reach Aldebaran, a reddish star
- Look above the belt for Betelgeuse, a red star
- Look below the belt for Rigel, a bright blue star
So the belt works like a signpost in the sky.
Why people care about it
People across cultures noticed these same three stars and made stories about them. They show up in ancient myths, religious texts, poetry, and early astronomy. The reason is simple: they’re impossible to miss.